The Role of Hybrid Education in Medical Education After COVID-19
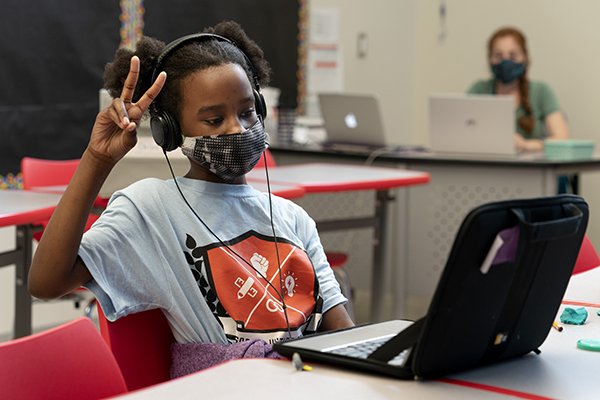
Maintaining student interaction during the extraordinary COVID-19 pandemic was a major problem for medical education. An investigation by the All India Institute of Medical Science (AIIMS), New Delhi, clarified the significance of hybrid education for both undergraduate and graduate medical education. Structured virtual group discussion (SVGD), a novel strategy that was adopted in postgraduate physiology education to solve the issue of low engagement, has proven to be a successful instrument for academic learning. The relevance of hybrid education in medical education during difficult times is highlighted in this article, which examines the results of the AIIMS study.
The Function Of Hybrid Education in Medical Education
The difficulties in medical education during the COVID-19 epidemic have been addressed through hybrid education, which blends in-person and online learning techniques. The implementation of virtual learning platforms became crucial as a result of the requirement to preserve social distance and reduce physical encounters. But it soon became clear that virtual learning on its own lacked the engagement required for efficient academic learning. This led AIIMS’s postgraduate programme in physiology to introduce structured virtual group discussions (SVGD).
Virtual Group Discussion with Structure (SVGD) in Hybrid Education
SVGD is a cutting-edge method that permits controlled, supervised, and unsupervised interactions amongst pupils. Synchronous and asynchronous interactions are both included in SVGD, which encourages active participation and improves the educational process. It keeps the advantages of in-person interactions while enabling students to take part in group discussions electronically.
Students’ perspectives of the SVGD
Students believed that SVGD was a more effective format than traditional group discussions held in a totally virtual environment, according to a study by AIIMS. Students had a foundation for insightful discussions and group learning thanks to SVGD’s structure. The active participation encouraged by SVGD resulted in a deeper comprehension of the material and encouraged critical thinking abilities.
Recognition and Study’s Impact of Hybrid Education
A respected worldwide publication of medical education published the findings of the study undertaken by AIIMS. The Association of Physiologists and Pharmacologists recognised the work and gave it the coveted Dev Raj Bajaj Award for the invention of novel methods in 2021. The research by Dr. Simran Kaur, Dr. Dinu S Chandran, Dr. Megha Bir, and Prof. KK Deepak at the Department of Physiology, AIIMS, New Delhi, has led to an innovation in medical education that has attracted attention for its potential to transform small-group teaching in undergraduate and postgraduate medical education.
Hybrid Education : The Future of Education
The results of the AIIMS study emphasize the value of hybrid learning for undergraduate and graduate medical education. The opportunity to bridge the divide between conventional in-person instruction and online learning environments is unique to hybrid education. Combining the two educational approaches can increase inclusivity, accommodate various learning preferences, and produce better functional results in postgraduate medical education.
Diversity of Learning Styles is Included in Hybrid Education
The flexibility of hybrid education to accommodate various learning styles is one of its main benefits. Others may find virtual learning more suited to their learning preferences than others, even though some students thrive in traditional classroom settings. Through hybrid education, both groups of students are guaranteed to gain from a mixed approach, enabling them to interact with the subject matter according to their unique needs.
Increasing Functional Results of Hybrid Education
The opportunity to improve functional outcomes in postgraduate medical education is provided by hybrid education. Educators can add interactive simulations, digital patient interactions, and other resources into the curriculum by utilizing the advantages of technology. These resources offer an engaging learning environment that helps students build crucial clinical skills and prepares them for real-world situations.