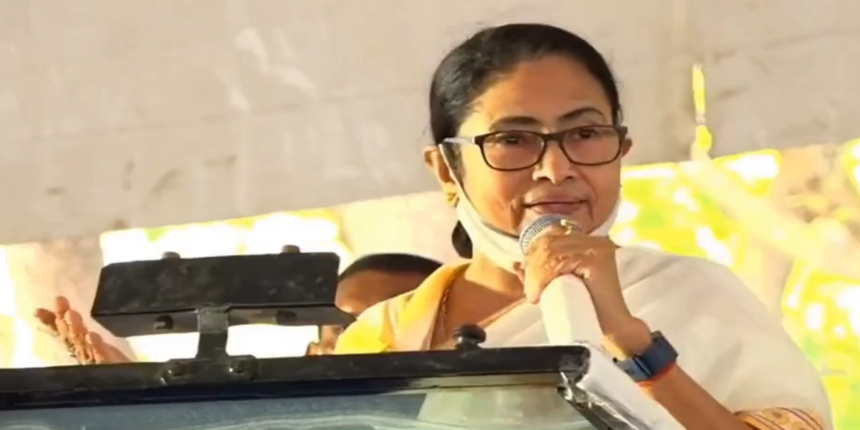
Mamata Banerjee, the chief minister of West Bengal, recently proposed the introduction of a 3-year undergraduate diploma in medicine. This idea has sparked controversy in Kolkata. This idea aims to address the state’s physician shortage. The state would provide this diploma programme concurrently with the current MBBS programme. However, this idea has aroused discussion and prompted worries among several parties.
The Demand for a Diploma Programme
Mamata Banerjee, West Bengal’s health minister, emphasised that the standard MBBS programme requires a minimum of five years to complete in order to produce a medical graduate. She is adamant that the creation of a diploma programme in medicine would resolve the state’s present physician shortage. Through this alternative route, people may train to become semi-doctors who could deliver basic medical care while being supervised by senior nurses and doctors.
Addressing the Shortage: Banerjee’s Recommendations
CM Banerjee made many recommendations in a Utkarsh Bangla review meeting to address the lack of doctors in West Bengal. She emphasised the five-year medical training program’s length and the use of junior doctors in various hospitals while they are still in school. Banerjee suggested creating a three-year certificate programme that would allow doctors to work in primary healthcare facilities as a solution to this problem. She also advised hiring experienced medical professionals and professors to instruct students enrolled in the diploma programme, ensuring the delivery of high-quality healthcare services.
MBBS seats and diploma programmes are being developed concurrently
Banerjee emphasised the significance of concurrent development in the field of medical education. The ability to teach doctors is growing along with the number of MBBS seats and medical colleges. In addition, a stronger healthcare infrastructure is required due to the expanding population and patient population. Banerjee advocated the creation of a certificate programme to help Bengal’s basic health infrastructure overcome these difficulties. She expressed her belief that this strategy will be successful in addressing the doctor shortage.
The Function of Diplomate Physicians in Primary Care
According to Banerjee, the primary healthcare sector would gain from the implementation of a parallel system of diploma doctors in addition to standard medical education. She emphasised the extensive coursework and several tests that future doctors must pass. These people will be able to work in primary healthcare, delivering necessary services like dispensing oxygen, life-saving medications, and saline under the supervision of experienced doctors and senior nurses, by developing a parallel system for obtaining diploma doctors.
Investigating legal issues and creating laws
Banerjee has charged the state’s health secretary, NS Nigam, with investigating the legal ramifications of the proposed diploma course’s implementation in order to assure its feasibility. This action indicates the government’s dedication to carefully assessing the proposal’s viability and potential effects. Banerjee has also recommended looking into the potential of drafting legislation that would elevate senior nurses to the level of “semi-doctors” for training reasons, thereby improving their capacity to assist with healthcare services.
Concerns and reservations
Despite the attention and discussion the initiative has received, a number of parties have also voiced their misgivings and worries. Critics contend that a 3-year diploma might not offer enough education and work experience to produce qualified physicians. They stress the value of a thorough and demanding medical education, which the conventional MBBS programme provides. Some interested parties are concerned that diploma doctors might not have the expertise and understanding required to adequately manage complex medical issues.
Examination of the three-year diploma course proposal in West Bengal’s healthcare system, with opposition and reconsideration demanded
The Problem with Quality Training
A professor at KPC Medical College & Hospital named Dr. Tirthankar Guha Thakurata raises questions about the calibre of training diploma doctors will receive throughout the planned three-year programme. He queries who would be in charge of instructing in these diploma institutions and provides assurances regarding the calibre of instruction and training they provide. Dr. Thakurata expressed concern over the potential emergence of subpar institutions that would turn out graduates unprepared to offer quality medical care. This casts considerable doubt on the proposed diploma program’s ability to alleviate West Bengal’s doctor deficit and provide high-quality healthcare.
Dr. Arindam Biswas: There is opposition based on unfairness and shortcuts
Dr. Arindam Biswas, a well-known general physician in the city, makes two compelling arguments against the plan. First of all, he thinks that the three-year diploma programme is a quick fix that cannot ensure the delivery of high-quality education and training. In order to guarantee the best levels of medical care, Dr. Biswas emphasises the crucial role of the healthcare industry, which calls for a strong and long-term approach.
Second, Dr. Biswas concerns why the diploma programme is being implemented primarily in West Bengal’s rural primary health centres. He contends that doing so results in an unfair contrast between healthcare systems in rural and urban areas. The authority in charge of assuring the calibre of instruction in institutions offering such diploma courses is another issue brought up by Dr. Biswas. He expresses his historical scepticism towards such initiatives by making reference to a similar suggestion made by the last Left Front administration that was flatly rejected.
Making sure there are checks and balances: Dr. Srijon Mukherjee’s View
A well-known maxillofacial surgeon named Dr. Srijon Mukherjee thinks that the implementation of diploma programmes in medicine is only possible with a thorough system of checks and balances. He suggests that students who have finished their higher secondary education in the science stream with a minimum of 60% should only be admitted to these courses. Dr. Mukherjee also emphasises the requirement for an authorised agency in charge of accrediting institutions that offer diploma courses. He also recommends limiting diploma doctors’ treatment options in some areas and putting in place a stringent oversight programme to make sure they follow the rules.
A panel has been established to investigate the introduction of a medicine diploma programme.
The panel’s composition
There are 14 people on the panel established to assess the viability of establishing a diploma programme in medicine. Respected senior physicians and representatives from illustrious medical organisations like the West Bengal Medical Council (WBMC) and the Indian Medical Association (IMA) are among the members of this diversified group. The panel’s makeup guarantees a thorough evaluation of all relevant consequences and aspects of conducting the diploma course.
Goals of the Panel Assessing Infrastructure and Feasibility
The main goal of the panel is to determine if a medical diploma programme might be implemented within West Bengal’s current healthcare system. This involves assessing the availability of the materials, instructors, and training facilities needed to carry out the programme successfully. The panel hopes to uncover any potential issues or gaps that require attention by examining the existing condition of healthcare education.
Designing and accrediting curriculum
The panel’s creation of an all-encompassing curriculum for the planned diploma course is another important goal. To ensure that students are sufficiently prepared for real-world healthcare problems, this curriculum should include both academic knowledge and practical training. The accreditation procedure, which verifies that the diploma programme complies with national norms and regulations, will also be covered by the panel.
Impact on Access to Healthcare
The panel will look at how the diploma programme can affect access to healthcare, particularly in rural areas. The course aims to increase the number of healthcare professionals accessible to assist underserved communities by providing people with the essential skills. The panel will examine any potential benefits, including decreased patient-to-doctor ratios, higher-quality healthcare, and expanded access to medical services.