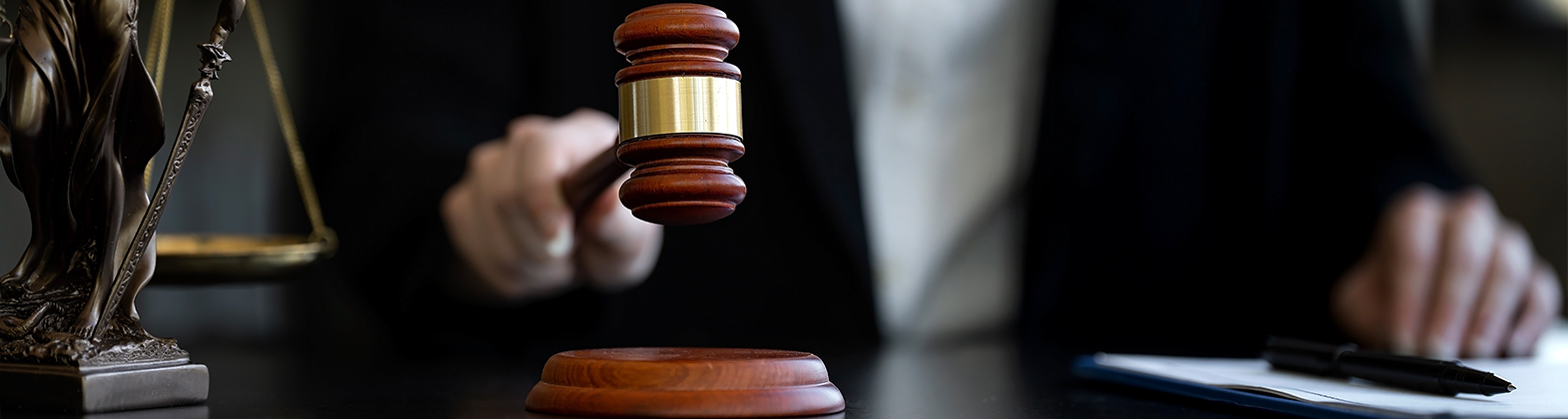
What is LLB?
The Bachelor of Laws (LLB) is one of the most respected and versatile undergraduate degrees globally, forming the cornerstone of legal education. It serves as a stepping stone for aspiring legal professionals who wish to pursue a career in law. This comprehensive guide by Bodmas Education explores what LLB is, its significance, the curriculum, career prospects, and much more.
Understanding LLB
Definition of LLB
The abbreviation LLB stands for “Legum Baccalaureus,” a Latin term meaning Bachelor of Laws. It is an undergraduate degree that provides comprehensive education and training in various fields of law. The LLB program aims to develop critical thinking, analytical skills, and a deep understanding of legal principles and systems.
History and Evolution
The LLB degree has its origins in the English legal system and has evolved over centuries. It has been adopted by many countries worldwide, each tailoring the curriculum to meet its legal system’s requirements. The degree remains a fundamental qualification for those seeking to practice law.
Importance of LLB
Foundational Knowledge
The LLB program provides a solid foundation in legal principles, doctrines, and systems. It covers various branches of law, such as constitutional law, criminal law, contract law, and property law, equipping students with a broad understanding of the legal landscape.
Critical Skills Development
An LLB degree develops essential skills such as critical thinking, problem-solving, and effective communication. These skills are not only vital for legal practice but also highly transferable to other fields.
Professional Qualification
For those aiming to become lawyers, judges, or legal advisors, an LLB is a necessary qualification. It is the first step towards further legal education and professional training, such as the Bar exam or legal practice courses.
Structure and Curriculum of LLB
Duration
The duration of an LLB program typically ranges from three to five years, depending on the country and the mode of study. In India, for instance, the LLB can be pursued as a three-year course for graduates or a five-year integrated course for students after 10+2.
Core Subjects
The LLB curriculum includes a mix of compulsory core subjects and electives. Key core subjects generally include:
- Constitutional Law: Study of the constitution, its interpretation, and the functioning of government bodies.
- Criminal Law: Examination of criminal behavior, legal processes, and criminal justice system.
- Contract Law: Principles governing contracts, agreements, and obligations.
- Tort Law: Laws related to civil wrongs and personal injuries.
- Property Law: Legal aspects of ownership, transfer, and use of property.
- Family Law: Laws concerning family relationships, marriage, divorce, and child custody.
Elective Subjects
Students can choose from various elective subjects to specialize in areas of interest, such as:
- Corporate Law: Laws governing businesses and corporations.
- Environmental Law: Legal frameworks for environmental protection and regulation.
- Human Rights Law: Protection and enforcement of individual and group rights.
- Intellectual Property Law: Laws related to patents, trademarks, and copyrights.
- International Law: Legal principles governing international relations and treaties.
Practical Training
LLB programs often include practical training components such as internships, moot court competitions, legal aid clinics, and workshops. These experiences provide hands-on learning and exposure to real-world legal practice.
Admission Requirements for LLB
Educational Qualifications
To enroll in an LLB program, candidates typically need to meet the following educational requirements:
- For 5-Year LLB: Completion of higher secondary education (10+2) with a minimum percentage (usually between 45% to 60%) from a recognized board.
- For 3-Year LLB: A bachelor’s degree in any discipline from a recognized university with a minimum required percentage.
Entrance Exams
Admission to LLB programs often requires candidates to clear entrance exams. Some of the prominent entrance exams include:
- CLAT (Common Law Admission Test): For admission to National Law Universities in India.
- AILET (All India Law Entrance Test): Conducted by National Law University, Delhi.
- LSAT (Law School Admission Test): Used by various law schools in India and worldwide.
- University-Specific Exams: Such as DU LLB Entrance Exam (Delhi University) and BHU UET (Banaras Hindu University).
Additional Requirements
Some universities may also consider additional criteria such as:
- Personal Statement: Explaining the candidate’s interest in law and career goals.
- Letters of Recommendation: From teachers or professionals attesting to the candidate’s suitability for a law program.
- Interview: Some institutions may conduct interviews as part of the selection process.
Career Opportunities After LLB
Legal Practice
An LLB degree opens up various career opportunities in the legal field:
- Advocate: Represent clients in courts, provide legal advice, and draft legal documents.
- Corporate Lawyer: Work in the legal departments of corporations, handling mergers, acquisitions, compliance, and other business-related legal matters.
- Public Prosecutor: Represent the state in criminal cases and ensure justice is served.
- Legal Advisor: Provide legal guidance to organizations, government bodies, or individuals.
Judiciary
Graduates can pursue a career in the judiciary by appearing for judicial service exams to become:
- Judge: Preside over court proceedings and deliver judgments.
- Magistrate: Handle lower-level judicial responsibilities in criminal and civil cases.
Academia and Research
LLB graduates can also choose to enter academia or legal research:
- Professor: Teach law at universities and colleges.
- Researcher: Conduct legal research and contribute to academic journals and publications.
Public Sector and Civil Services
- Civil Servant: Appear for civil services exams and work in various administrative roles in the government.
- Legal Consultant: Provide legal expertise to government agencies and public sector undertakings.
Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs)
- Legal Consultant: Work with NGOs to provide legal aid, advocacy, and support for social causes.
- Human Rights Activist: Work on issues related to human rights, social justice, and public interest litigation.
How Bodmas Education Can Help
Navigating the complexities of pursuing an LLB degree can be challenging. Bodmas Education offers expert guidance and support to aspiring law students:
Comprehensive Counseling
Our experienced counselors provide personalized advice on:
- Choosing the Right Program: Helping you select the best LLB program and university based on your career goals and preferences.
- Entrance Exam Preparation: Offering coaching and resources to prepare for various law entrance exams.
- Application Assistance: Guiding you through the application process, including document preparation, personal statements, and interviews.
Financial Planning
Bodmas Education assists with:
- Scholarship Guidance: Identifying and applying for scholarships and financial aid.
- Education Loans: Helping you secure education loans to cover tuition fees and other expenses.
Career Support
We provide ongoing support to help you achieve your career aspirations:
- Internship and Placement Assistance: Connecting you with internships and job opportunities in the legal field.
- Networking Opportunities: Facilitating connections with legal professionals and alumni.
Expert Guidance for LLB Degree
The LLB degree is a gateway to a rewarding and versatile career in law. It provides a solid foundation in legal principles, critical skills development, and numerous career opportunities. With the right guidance and support from Bodmas Education, you can navigate the path to becoming a successful legal professional.
For personalized assistance and expert guidance on pursuing an LLB degree, contact Bodmas Education. Our dedicated team is here to help you every step of the way, ensuring you achieve your academic and career goals in the field of law.